Section 1 RACII
Section 2 POWER INFLUENCE
Section 3 NETWORK RELATIONSHIP MODEL - IT'S WHO YOU KNOW
Section 4 CIRCLES OF INFLUENCE MODEL- ITS WHAT YOU CAN IMPACT
Section 5 DISC - INFLUENCE MODEL
Section 6 THINKING AND BEHAVOUR STYLE AND INFLUENCE - MBTI
Section 7 TEAM NETWORKS, COMMUNICATIONS AND INFLUENCE
Section 8 HOW TO WIN FRIENDS AND INFLUENCE PEOPLE
Section 9 NANCY KLINE - TIME TO THINK
Section 10 COMMUNICATIONS CALENDAR
I hope I have attributed and named all the models correctly, and I have been careful to include all the links to the resources. I welcome comments or corrections and suggested additions.
If you are interested in Strategy, Projects, Programmes or Change please contact Tim@AdaptConsultingCompany.com or phone +44(0)7797762051

Key Points
It is about communication, consultation, roles and responsibilities. There are many variations on this theme- Responsible: People or stakeholders who do the work. They must complete the task or objective or make the decision. Several people can be jointly Responsible.
- Accountable: Person or stakeholder who is the "owner" of the work. He or she must sign off or approve when the task, objective or decision is complete. This person must make sure that responsibilities are assigned in the matrix for all related activities. Success requires that there is only one person Accountable, which means that "the buck stops there."
- Consulted: People or stakeholders who need to give input before the work can be done and signed-off on. These people are "in the loop" and active participants.
- Informed: People or stakeholders who need to be kept "in the picture." They need updates on progress or decisions, but they do not need to be formally consulted, nor do they contribute directly to the task or decision.
Comments
I always use this when project planning roles, goals, consultation and stakeholders. There many variations on this theme, and you may want to add elements to suit the project or context.Useful Links
https://www.solitaireconsulting.com/2020/07/stakeholder-management-using-the-power-interest-matrix/
https://www.24point0.com/ppt-shop/raci-matrix-powerpoint/
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Responsibility_assignment_matrix

Key Points
It is about keepin the right stakeholders informed according to their power/influence- High power, highly interested people (Manage Closely): you must fully engage these people, and make the greatest efforts to satisfy them.
- High power, less interested people (Keep Satisfied): put enough work in with these people to keep them satisfied, but not so much that they become bored with your message.
- Low power, highly interested people (Keep Informed): adequately inform these people, and talk to them to ensure that no major issues are arising. People in this category can often be very helpful with the detail of your project.
- Low power, less interested people (Monitor): again, monitor these people, but don’t bore them with excessive communication.
Comments
This is interesting because it is political and practical: it is ostensibly about lobbying for resources or canvassing for approval. There are implications with this model if you consider that the aim is not to satisfy people in each square, but to move them to the square where you want them to be.- If they are LOW power but you want them to be HIGH power, give them a role, promote them, showcase them, give then formal authority (budget holder, expert, sponsor) or informal authority (rapporter, scribe, facilitator)
- If they are HIGH power but you want them to be LOW power, minimise their interest by distracting them with other tasks or overloading them with meaningless tasks, or simply excluding them from facts, conversations and meetings effectively marginalising them and making them inconsequential or discredited to the decision process.
- If they are HIGH influence but you want them to be LOW influence, minimise their interest by distracting them with something more important, assure them "there is nothing to see" or "nothing to worry about" either reduce their interest in the topic or reduce the topics interest to them.
- If they are LOW influence but you want them to be HIGH influence, maximise their interest by pointing out impact or implications, assure them "this is important" or "this is an opportunity" either increase their interest in the topic (briefings, meetings, data) or increase the topics interest to them (opportunity to advance, pay, prestige etc.)
Useful Links
https://www.solitaireconsulting.com/2020/07/stakeholder-management-using-the-power-interest-matrix/
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Stakeholder_analysis
Key Points Six degrees of separation is the idea that all people on average are six, or fewer, social connections away from each other. Also known as the 6 Handshakes rule. As a result, a chain of "a friend of a friend" statements can be made to connect any two people in a maximum of six steps. When we understand this we realise how we can leverage our network of who knows who, so that when it comes to influence or persuasion where we might not have a direct affect we may, though use of the network have an indirect, but nonetheless profound effect.
Comments
When planning one project we spend a lot of time on who knows who, so that we could create a cascade of super-communicators. For example my telling Person A something we knew they would tell Persion 1,2,3,4,5,6 and my telling Person B something we knew they would tell Persion 7,8,9,10,11. By understanding the cascade network of influence you only have directly communicate with 10 to be able to influence up to 100 (or more).Our choice was not solely based on Person A knows 10 people and Person B knows 10 other people. We noted for example that Person A had a style, authority, approach which would go very well with Persion 1,2,3,4,5,6 and Person B had a style, authority, approach which would work with Persion 7,8,9,10,11.
This approach of matching select messages with key messengers really helped our project and change delivery.
Useful Links
https://agileleanlife.com/relationship-circles/
https://www.thera.co.uk/content/uploads/2017/04/Safe-and-Secure-Worksheet-4.pdf
https://www.dis-sos.com/circles-of-relationships/

Grant me the serenity to accept the things I cannot change, courage to change the things I can, and wisdom to know the difference.
Key Points
The CIRCLES OF INFLUENCE might be regarded in the context of the Serenity Prayer: Grant me the serenity to accept the things I cannot change, courage to change the things I can, and wisdom to know the difference.However I am going to apply this model very differently. Persuasion and Influence can be very complex. Let's take buying a computer. You might think there are 2 people involved: seller and buyer. But careful thought tells us that the following people might be involved. Understanding their needs and communicating in their terms may have a profound effect on the outcome. Thus you can work to engage or disengage people's interest or concern or move things into or out-of their control by the way you approach your communications.
- The sponsor may be interested in the cost or budget
- The finance person may be interested in the return on investment
- The technology person may be interested in compatibility and security
- The manager may be interested in functionality
- The end-users may be interested in ease of use
- The risk team maybe concerned about data and privacy
- The HR team may be interested in support and training
- The investors may be interested in market response
Comments
This is classic stakeholder management: understanding the "hot topic" for each group and managing the message content, media, style, timing to meet our plans for that person. This may be to influence or persuade positively or negatively. When we know who has formal power (because of hierarchy) or technical power (because of expertise) or persuasive power (because of like-ability) or resource power (because they control access to people, materals or funds) or approval power (because they sign-off eg risk or compliance) we can move them around the board like chess pieces based on message content, media, style, timing. This is how political campaigns are fought and won, knowing who is "for" who is "against" and what are the factors that will influence the critical "undecided"Useful Links
https://www.abrahampc.com/blog/2020/3/16/what-can-i-do-the-circles-of-concern-and-influence
https://dplearningzone.the-dp.co.uk/wp-content/uploads/sites/2/2015/06/Covey.pdf
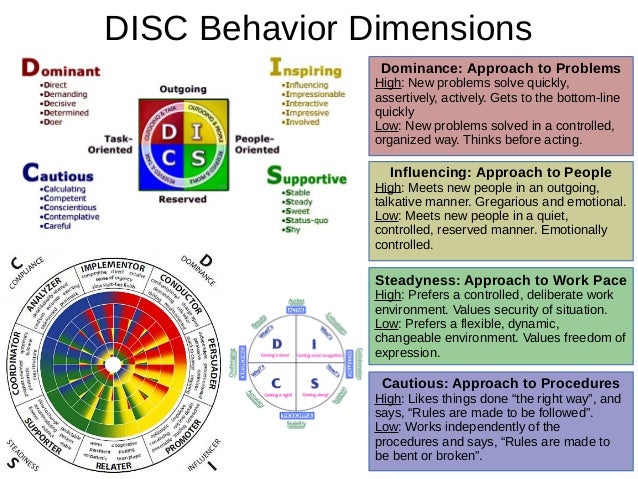
Key Points
Much has already been said about matching the right communication style and content to each person. Understanding the DISC communication preferences helps us undserstand how people like to receive and process information and consequently how we might best persuade or influence.- the DOMINANT type is also known as High D: Outgoing and Task-oriented Dominant Style: People who have both Outgoing and Task-oriented traits often exhibit DOMINANT and DIRECT behaviors. They usually focus on results, problem-solving, and the bottom-line.
- the INSPIRING type is also known as High I: Outgoing and People-oriented Inspiring Style: People who have both Outgoing and People-oriented traits often exhibit INSPIRING and INTERACTIVE behaviors. They usually focus on interacting with people, having fun, and/or creating excitement.
- the SUPPORTIVE type is also known as High S: Reserved and People-oriented Supportive Style: People who have both Reserved and People-oriented traits often exhibit SUPPORTIVE and STEADY behaviors. They usually focus preserving relationships and on creating or maintaining peace and harmony.
- the CAUTIOUS type is also known as High C: Reserved and Task-oriented Cautious Style: People who have both Reserved and Task-oriented traits often exhibit CAUTIOUS and CAREFUL behaviors. They usually focus on facts, rules, and correctness.
Useful Links
https://discpersonalitytesting.com/free-disc-test/
http://blog.extendeddisc.org/disc-communication-styles
https://www.discprofile.com/what-is-disc
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/DISC_assessment
Understanding MBTI means understanding the following
- Favorite world: Do you prefer to focus on the outer world or on your own inner world? This is called Extraversion (E) or Introversion (I).
- Information: Do you prefer to focus on the basic information you take in or do you prefer to interpret and add meaning? This is called Sensing (S) or Intuition (N).
- Decisions: When making decisions, do you prefer to first look at logic and consistency or first look at the people and special circumstances? This is called Thinking (T) or Feeling (F).
- Structure: In dealing with the outside world, do you prefer to get things decided or do you prefer to stay open to new information and options? This is called Judging (J) or Perceiving (P).

Key Points
The MBTI style suggests to us the communication preferences helps us undserstand how people like to receive and process information and consequently how we might best persuade or influence.With ST people: Be specific, confident, well-reasoned demonstrate immediate advantages, profit provide examples; use visual aids.
With NT people: Be specific, well-reasoned; use visual aids, diagrams use concepts, theories appeal to intellectual capabilities give them a challenge show how the problem in hand or subject of communication fits into the "big picture"
With SF people: Be supportive, expressive, and confident provide examples; demonstrate immediate advantages, profit appeal to feelings and emotions
With NF people: Be expressive, well-reasoned use visual aids use concepts, theories appeal to their intuition give them a challenge show how the problem in hand or subject of communication fits into the "big picture"
Comments
I use this or a variation on all projects and change programmes and then link to communications plan of what gets said to whom, why, when and how. This is essential understanding for persuasion and influence in projects and change.Useful Links
http://www.humanmetrics.com/personality/communication-strategies-for-different-types
https://www.verywellmind.com/the-myers-briggs-type-indicator-2795583
Key Points
It is important to understand that the bigger the team the harder it is to maintain communications essential understanding for persuasion and influence in projects and change.Comments
I try to keep teams small 5 to 7 people. If there are more, have a sub-team. There is no reason not have have a team of teams.Useful Links
https://brainleaf.com/blog/development/planning-for-complexity-in-project-scoping/
The book HOW TO WIN FRIENDS AND INFLUENCE PEOPLE is a classic
Key Points
Six Ways to Make People Like You
- Become genuinely interested in other people. "You can make more friends in two months by being interested in them, than in two years by making them interested in you."[6]:52 The only way to make quality, lasting friendships is to learn to be genuinely interested in them and their interests.
- Smile. Happiness does not depend on outside circumstances, but rather on inward attitudes. Smiles are free to give and have an amazing ability to make others feel wonderful. Smile in everything that you do.
- Remember that a person's name is, to that person, the sweetest and most important sound in any language. "The average person is more interested in their own name than in all the other names in the world put together." People love their names so much that they will often donate large amounts of money just to have a building named after themselves. We can make people feel extremely valued and important by remembering their name.
- Be a good listener. Encourage others to talk about themselves. The easiest way to become a good conversationalist is to become a good listener. To be a good listener, we must actually care about what people have to say. Many times people don't want an entertaining conversation partner; they just want someone who will listen to them.
- Talk in terms of the other person's interest. The royal road to a person's heart is to talk about the things he or she treasures most. If we talk to people about what they are interested in, they will feel valued and value us in return.
- Make the other person feel important – and do it sincerely. The golden rule is to treat other people how we would like to be treated. We love to feel important and so does everyone else. People will talk to us for hours if we allow them to talk about themselves. If we can make people feel important in a sincere and appreciative way, then we will win all the friends we could ever dream of.
Twelve Ways to Win People to Your Way of Thinking
- The only way to get the best of an argument is to avoid it. Whenever we argue with someone, no matter if we win or lose the argument, we still lose. The other person will either feel humiliated or strengthened and will only seek to bolster their own position. We must try to avoid arguments whenever we can.
- Show respect for the other person's opinions. Never say "You're wrong." We must never tell people flat out that they are wrong. It will only serve to offend them and insult their pride. No one likes to be humiliated; we must not be so blunt.
- If you're wrong, admit it quickly and emphatically. Whenever we are wrong we should admit it immediately. When we fight we never get enough, but by yielding we often get more than we expected. When we admit that we are wrong people trust us and begin to sympathize with our way of thinking.
- Begin in a friendly way. "A drop of honey can catch more flies than a gallon of gall." If we begin our interactions with others in a friendly way, people will be more receptive. Even if we are greatly upset, we must be friendly to influence people to our way of thinking.
- Start with questions to which the other person will answer yes. Do not begin by emphasizing the aspects in which we and the other person differ. Begin by emphasizing and continue emphasizing the things on which we agree. People must be started in the affirmative direction and they will often follow readily. Never tell someone they are wrong, but rather lead them where we would like them to go with questions that they will answer "yes" to.
- Let the other person do a great deal of the talking. People do not like listening to us boast, they enjoy doing the talking themselves. Let them rationalize and talk about the idea, because it will taste much sweeter to them in their own mouth.
- Let the other person feel the idea is his or hers. People inherently like ideas they come to on their own better than those that are handed to them on a platter. Ideas can best be carried out by allowing others to think they arrived at it themselves.
- Try honestly to see things from the other person's point of view. Other people may often be wrong, but we cannot condemn them. We must seek to understand them. Success in dealing with people requires a sympathetic grasp of the other person's viewpoint.
- Be sympathetic with the other person's ideas and desires. People are hungering for sympathy. They want us to recognize all that they desire and feel. If we can sympathize with others, they will appreciate our side as well and will often come around to our way of thinking.
- Appeal to the nobler motives. Everyone likes to be glorious in their own eyes. People believe that they do things for noble and morally upright reasons. If we can appeal to others' noble motives we can successfully convince them to follow our ideas.
- Dramatize your ideas. In this fast-paced world, simply stating a truth isn't enough. The truth must be made vivid, interesting, and dramatic. Television has been doing it for years. Sometimes ideas are not enough and we must dramatize them.
- Throw down a challenge. The thing that most motivates people is the game. Everyone desires to excel and prove their worth. If we want someone to do something, we must give them a challenge and they will often rise to meet it.
Be a Leader: How to Change People Without Giving Offense or Arousing Resentment
- Begin with praise and honest appreciation. People will do things begrudgingly for criticism and an iron-fisted leader, but they will work wonders when they are praised and appreciated.
- Call attention to people's mistakes indirectly. No one likes to make mistakes, especially in front of others. Scolding and blaming only serve to humiliate. If we subtly and indirectly show people mistakes, they will appreciate us and be more likely to improve.
- Talk about your own mistakes before criticizing the other person. When something goes wrong, taking responsibility can help win others to your side. People do not like to shoulder all the blame and taking credit for mistakes helps to remove the sting from our critiques of others.
- Ask questions instead of giving direct orders. No one likes to take orders. If we offer suggestions, rather than orders, it will boost others' confidence and allow them to learn quickly from their mistakes.
- Let the other person save face. Nothing diminishes the dignity of a man quite like an insult to his pride. If we don't condemn our employees in front of others and allow them to save face, they will be motivated to do better in the future and confident that they can.
- Praise every improvement. People love to receive praise and admiration. If we truly want someone to improve at something, we must praise their every advance. "Abilities wither under criticism, they blossom under encouragement."
- Give the other person a fine reputation to live up to. If we give people a great reputation to live up to, they will desire to embody the characteristics with which we have described them. People will work with vigor and confidence if they believe they can be better.
- Use encouragement. Make the fault seem easy to correct. If a desired outcome seems like a momentous task, people will give up and lose heart. But if a fault seems easy to correct, they will readily jump at the opportunity to improve. If we frame objectives as small and easy improvements, we will see dramatic increases in desire and success in our employees.
- Make the other person happy about doing what you suggest. People will most often respond well when they desire to do the behavior put forth. If we want to influence people and become effective leaders, we must learn to frame our desires in terms of others' desires.
Comments
The book How to Win Friends and Influence People is a classic, must read book. Highly recommended. i actually have a summary of the points above on a card that I keep in my diary. Often before a meeting I try and read it to remind me composure, confidence, context and conversation. I am far from perfect, but at least I am aware of my imperfections!Useful Links
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/How_to_Win_Friends_and_Influence_People
Coaching is a method to influence or persuade. This opens up a whole range of tools, models and approaches to influence or persuasion. However I will suggest one model only and perhaps make coaching, facilitation and mentoring a separate compendium of tools, models and approaches. The model I have selected is NANCY KLINE - TIME TO THINK, and below are the key factors to creating a thinking environment.
Key Points
- ATTENTION: listening with palpable respect and genuine interest, and without interruption. The quality of our attention determines the quality of other people’s thinking.
- EQUALITY: treating each other as thinking peers; giving equal turns and attention; Everyone is valued equally as a thinker.
- EASE: offering freedom from internal rush or urgency. Ease, an internal state free from rush or urgency, creates the best conditions for thinking.
- APPRECIATION: practicing a 5:1 ratio of appreciation to challenge. Because the brain requires appreciation to work well, our thinking is often specious.
- ENCOURAGEMENT: giving courage to go to the cutting edge of ideas by moving beyond internal competition. Competition between thinkers can be dangerous, replace it with a wholehearted, unthreatened search for good ideas.
- FEELINGS: allowing sufficient emotional release to restore thinking. We think that when feelings start, thinking stops. Instead, when people show signs of feelings, we relax and welcome them, good thinking will resume.
- INFORMATION: supplying the facts; recognising social context; dismantling denial. Accurate and full information provides the path to good independent thinking. Dismantling denial is often the first step to independent thinking.
- DIFFERENCE: welcoming diverse group identities and diversity of thinking. The greater the diversity of the group, and the greater the welcoming of different points of view, the greater the chance of accurate, cutting-edge thinking
- INCISIVE QUESTIONS: removing untrue assumptions that limit our ability to think for ourselves well. Challenge or remove untrue limiting assumption, lived as true.
- PLACE When the physical environment affirms our importance, we think more clearly and boldly. Thinking Environments are places that say back to people, ‘You matter.’ People think at their best when they notice that the place reflects their value.
Comments
I like NANCY KLINE - TIME TO THINK because it emphasises the context of communications (environment and attitude) is critical to the content of communications and this has to be a factor in better thinking, better decisions and influence or persuasion.Useful Links
https://www.customerinsightleader.com/books/book-review-time-to-think/
| When | Who | Hot Topic | Message | For / Against | Intention (Why) | Method | Done | Feedback |
| Planning | People | Key Topic | Gain Support | |||||
| Pilot | Teams | Reduce Resistance | Phone | |||||
| Approval | Media | Get Decision | Zoom or Teams | |||||
| Start | Union | Placate | Coffee Chat | |||||
| Middle | Shareholders | Website | ||||||
| End | Customers | Intranet | ||||||
| Review | Clients | One-to-One | ||||||
| Investors | Team Meeting | |||||||
| Public | Appraisal | |||||||
| | | | |
| When | Who | Hot Topic | Message | For / Against | Intention (Why) | Method | Done | Feedback |
| Planning | Shareholders | Money | Return on Investment | For +1 | Gain Support | Team Meeting | Yes dd/mm/yy | Key concerns, issues, actions |
| Planning | Customers | Price | Benefits | For +2 | Gain Support | Website | Yes dd/mm/yy | Key concerns, issues, actions |
| Planning | Union | Jobs | Opportunities | Against -1 | Gain Support | Coffee Chat | Yes dd/mm/yy | Key concerns, issues, actions |
| Planning | Teams | Work | Skills | Against -1 | Gain Support | Team Meeting | Yes dd/mm/yy | Key concerns, issues, actions |
| Pilot | Shareholders | Money | Return on Investment | For +1 | Gain Support | Team Meeting | Yes dd/mm/yy | Key concerns, issues, actions |
| Pilot | Customers | Price | Benefits | For +1 | Gain Support | Website | Yes dd/mm/yy | Key concerns, issues, actions |
| Pilot | Union | Jobs | Opportunities | For +1 | Gain Support | Coffee Chat | In Progress dd/mm/yy | Pending |
| Pilot | Teams | Work | Skills | For +1 | Gain Support | Team Meeting | Planned dd/mm/yy | TBC |
Key Points
The key point is, as noted above, managing the message content, media, style, timing to meet our plans for that person or group. Sometimes the order in which you tell people can be critical to success which is why leaks can be so troublesome. The above table is very simplistic, in truth you may have many people or representatives (more than simply customers, suppliers, staff, management, public and media), and many methods or media (more than simply emails, meetings, presentations, commercials, posters) and many stages or phases (more than simply start middle, end)Comments
I always do this for every project or change and it is often quite a bit more complex than this. For some large-scale public sector change this can include hundreds of stakeholders and thousands of messages. When working on messages we took the following approach to appeal to those who like brevity and those who like detail. We took effort to match the right message and level of detail to each person or group according to their preferences.For each topic
- One PHRASE or sentence that you can say in a lift, or as a sound-bite for TV or media
- One PARAGRAPH or summary that you can say to offer more information, context or detail, usually a follow-up to the above.
- One PAGE or detail that you can explain to demonstrate thinking, feeling, consultation, usually a follow-up to the above.
- One PACK or similar data-bundle or report to detail thinking, feeling, consultation, usually a follow-up to the above

No comments:
Post a Comment